
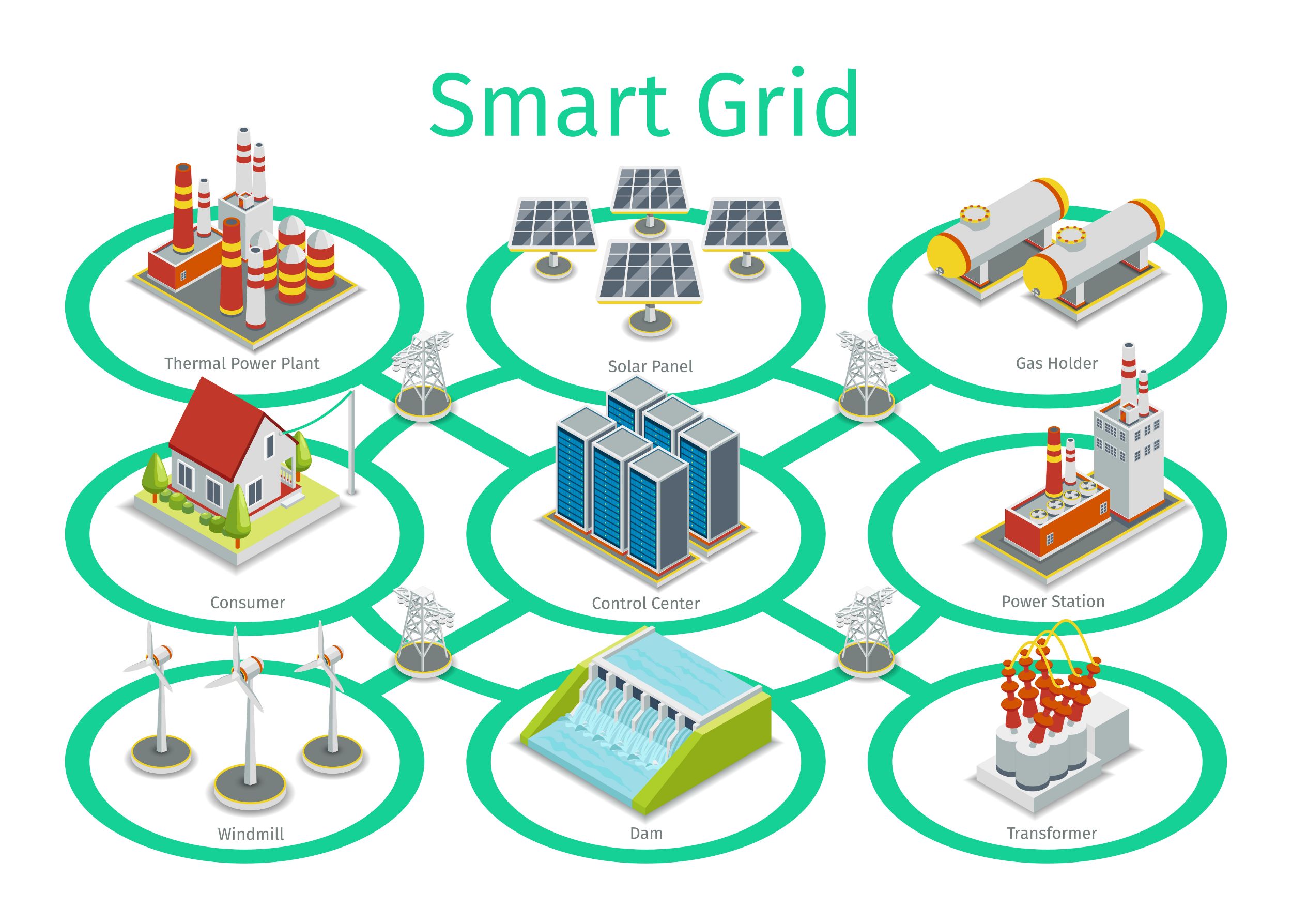
Therefore, potential problem points where the electric supply fails can be identified automatically. On the other hand, the smart grid is equipped to monitor the power flow. With the consumer feedback, the electric grid system can’t address any issue related to power flow because the system has no knowledge or visibility of whether consumers receive their electricity supply. This means that an electric grid has a reactive approach to managing power flow disparities as they are notified along the system. The electricity provider can only know there is an issue on the grid when consumers get in touch to complain. So what is a smart grid, and what do you need to know to build an effective smart grid solution?Ī conventional electric grid system lacks visibility of power flow failures and issues. Nowadays, the world counts over 9,200 grids, which are responsible for delivering approximately 1 million Megawatt power to a variety of consumers. Ultimately, the first electric grid appeared at the end of the 19th century. In reality, there are some crucial differences between the two, which are linked to the natural evolution of electric grids over time to meet the current needs of customers.

Most people are aware of the term “grid”, which refers to an electric grid, and assume that a smart grid and an electric grid are the same thing. There is a lot of confusion when it comes to discussing smart grid solutions. Multiple small grids rather than a single one.

Energy storage for variable energy sources.Renewable energy integration with an inverter.FSP’s smart grid solutions recommendations.What are the challenges of building the smart grid?.What are the benefits of building smart grid solutions?.What are the main features of a smart grid solution?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
